 Frontiers in Pharmacology
Frontiers in PharmacologyHBK-17, a 5-HT1A receptor ligand with anxiolytic-like activity, preferentially activates ß-arrestin signaling

The takeaway
HBK-17, a novel serotonin receptor ligand, shows anxiolytic-like effects in mice but primarily activates the β-arrestin pathway, offering a different mechanism compared to traditional anxiolytics.
The science
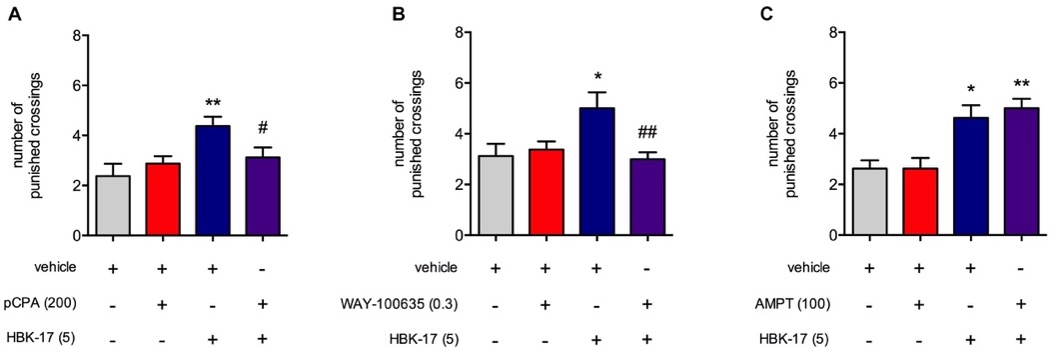
HBK-17 exhibits high affinity for 5-HT1A receptors and has moderate interactions with D2, while showing weak affinity for 5-HT7 receptors. In behavioral tests like the four-plate and elevated plus maze, it increased exploratory behavior without influencing pain sensitivity or movement, confirming its anxiolytic-like properties. This effect was absent after serotonin depletion or blockade of 5-HT1A receptors, highlighting the role of the serotonergic system. Cellular assays indicated that HBK-17 primarily promotes β-arrestin recruitment at 5-HT1A receptors rather than activating calcium or cAMP pathways. Pharmacokinetic data showed rapid absorption, brain access, and moderate bioavailability.
Why it matters
By biasing signaling through β-arrestin at 5-HT1A receptors, HBK-17 may provide anti-anxiety benefits with fewer side effects, highlighting biased agonism as a promising approach for next-generation anxiolytics.
Original article
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142499
Our other publications
The initiative focuses on promotion techniques that can revolutionize traditional research approaches pharmaceuticals.
 International Journal of Molecular Sciences
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Medicinal Research Reviews
Medicinal Research Reviews



